WITH CTEs let's resolve a (sub)query
CTEs, Common Table Expressions, are not too common but when you need them your expressions are too common. :)
So, what are CTEs and when should you use it over Subqueries?
A CTE (Common Table Expression) is a temporary result set that you can reference within a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement. CTEs are especially useful for
simplifying complex queries,
making code more readable,
and reducing the need for subqueries
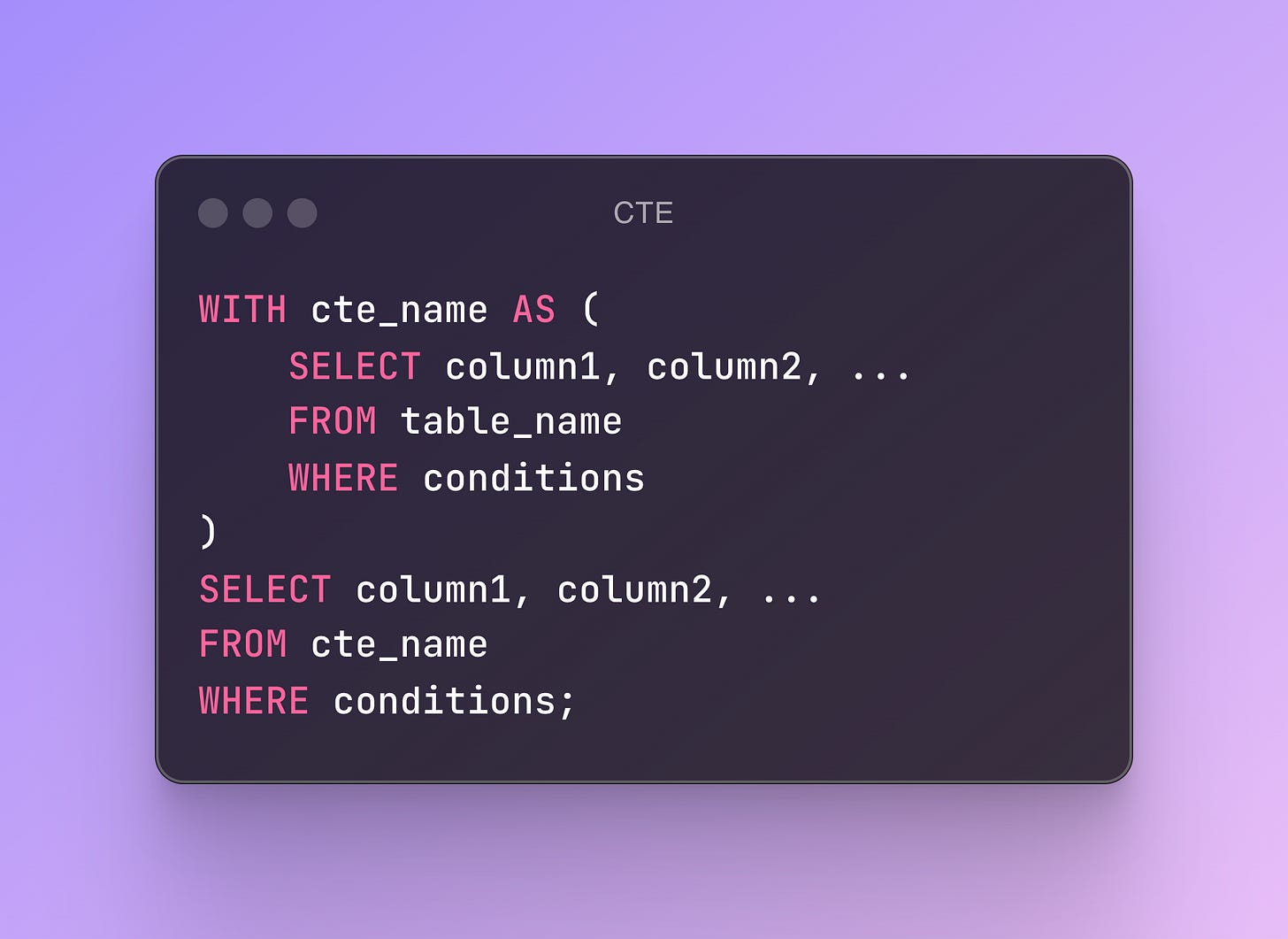
Format of a CTE:
The first CTE in your query must start with the keyword WITH
A CTE must be defined before it can be called
Separate multiple CTE's using commas
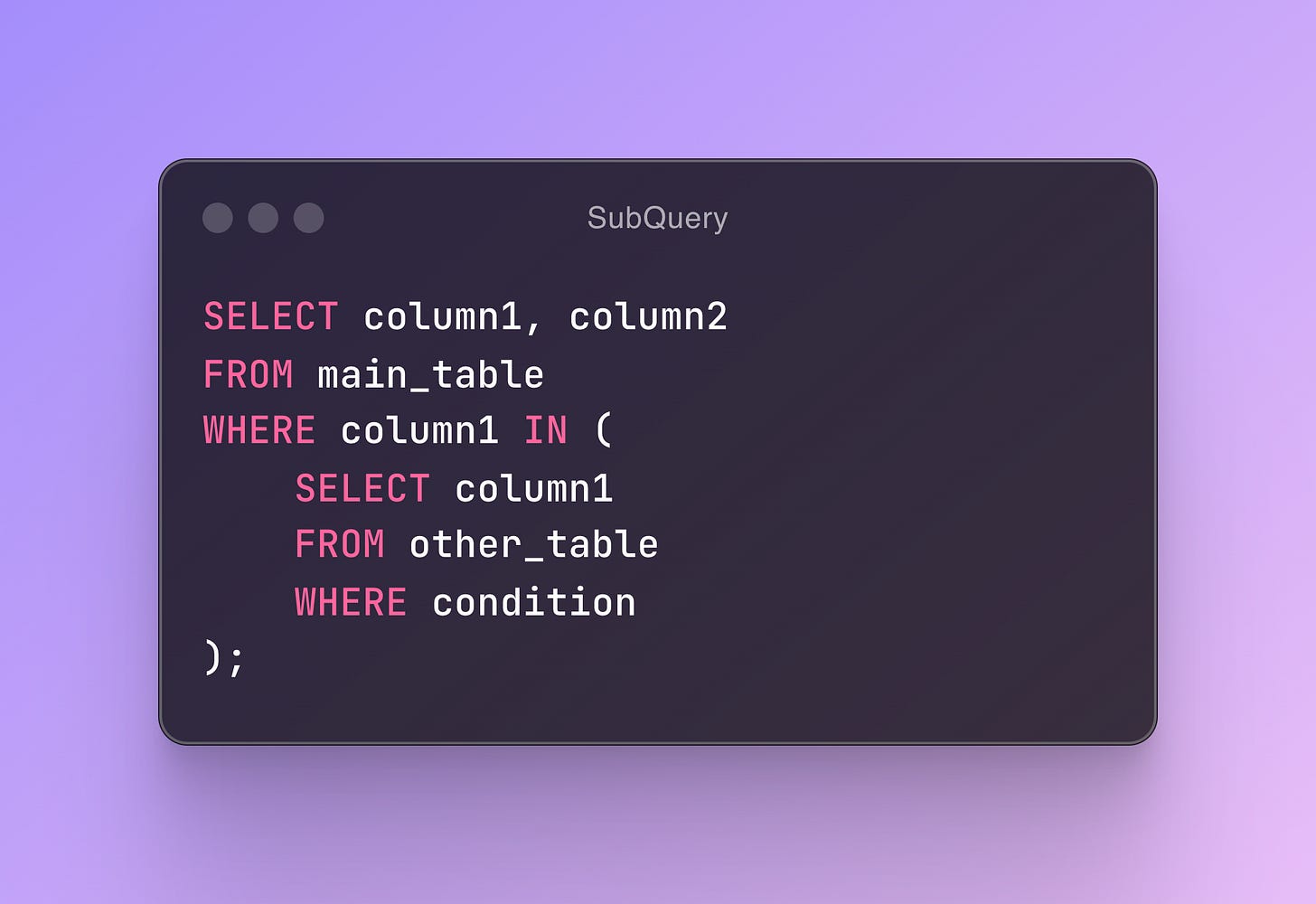
Format of a Subquery:
So, the question is - when to use one over another?
Use CTE when:
Improving Readability: CTEs make complex queries easier to understand by breaking down different parts into named, logical sections. This is especially useful when the query has multiple layers or repetitive subqueries
Reusing a Subquery: If the same subquery needs to be referenced multiple times within a query, a CTE can help you avoid rewriting it. This reduces the risk of errors and makes maintenance easier
Improving Performance on Complex Queries: In some cases, CTEs are more efficient than subqueries, especially if they involve multiple joins or aggregations, because the CTE can be evaluated once and reused
Use Subquery when:
Simple, One-Time Use: When you need a subquery only once, especially if it’s straightforward and doesn’t need reuse. For instance, if you’re just retrieving a single aggregated value for filtering, a subquery can be quicker and simpler.
Embedding in an Existing Query: If you need a one-off calculation that can be embedded directly into a larger query without reusing it elsewhere, a subquery is often appropriate.
Avoiding Overhead for Small Queries: In some SQL engines, CTEs can add a bit of overhead, as they are often materialized (calculated once and stored temporarily). For simple queries or where performance is critical and you don’t need the reuse benefits of a CTE, a subquery may be more efficient.
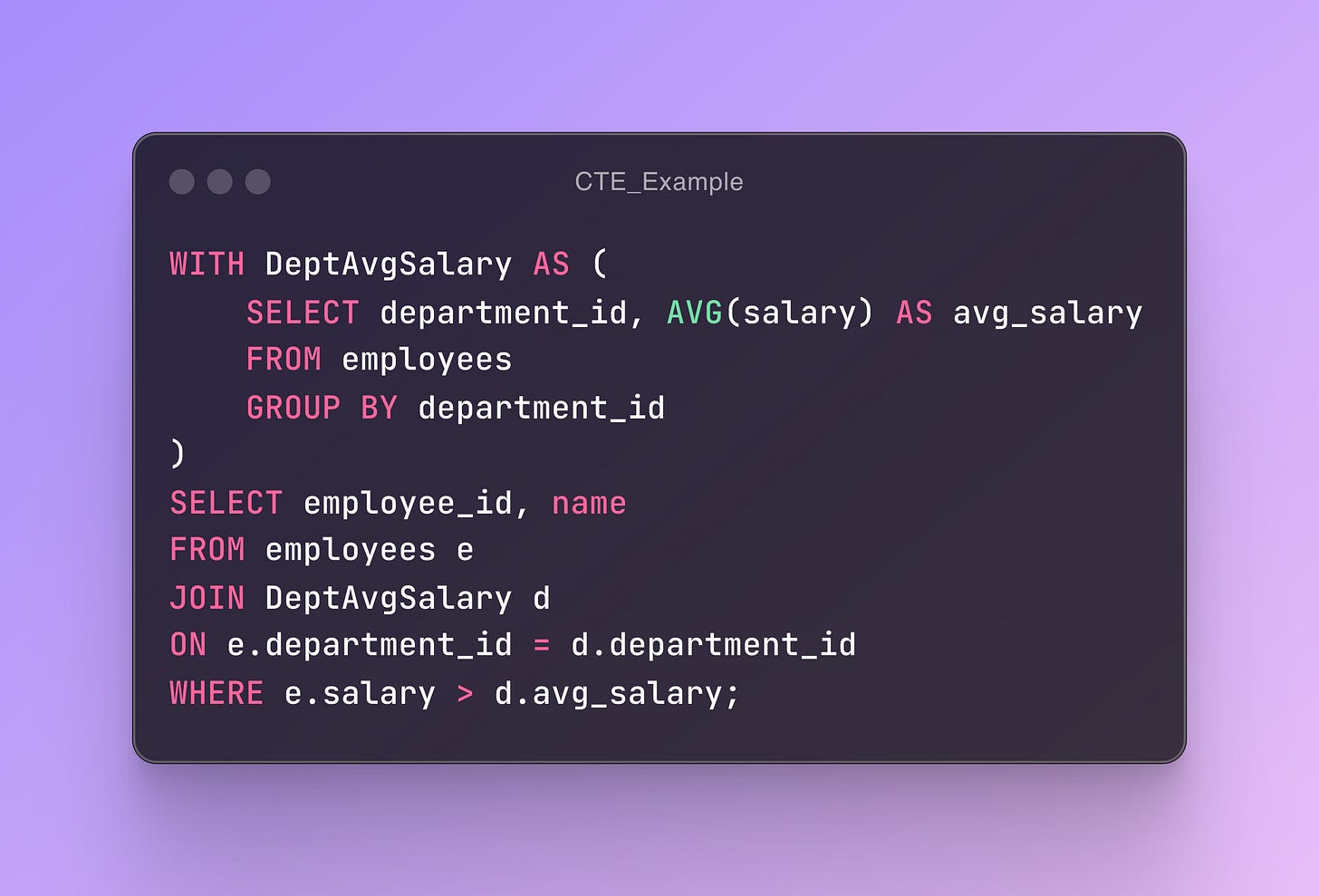
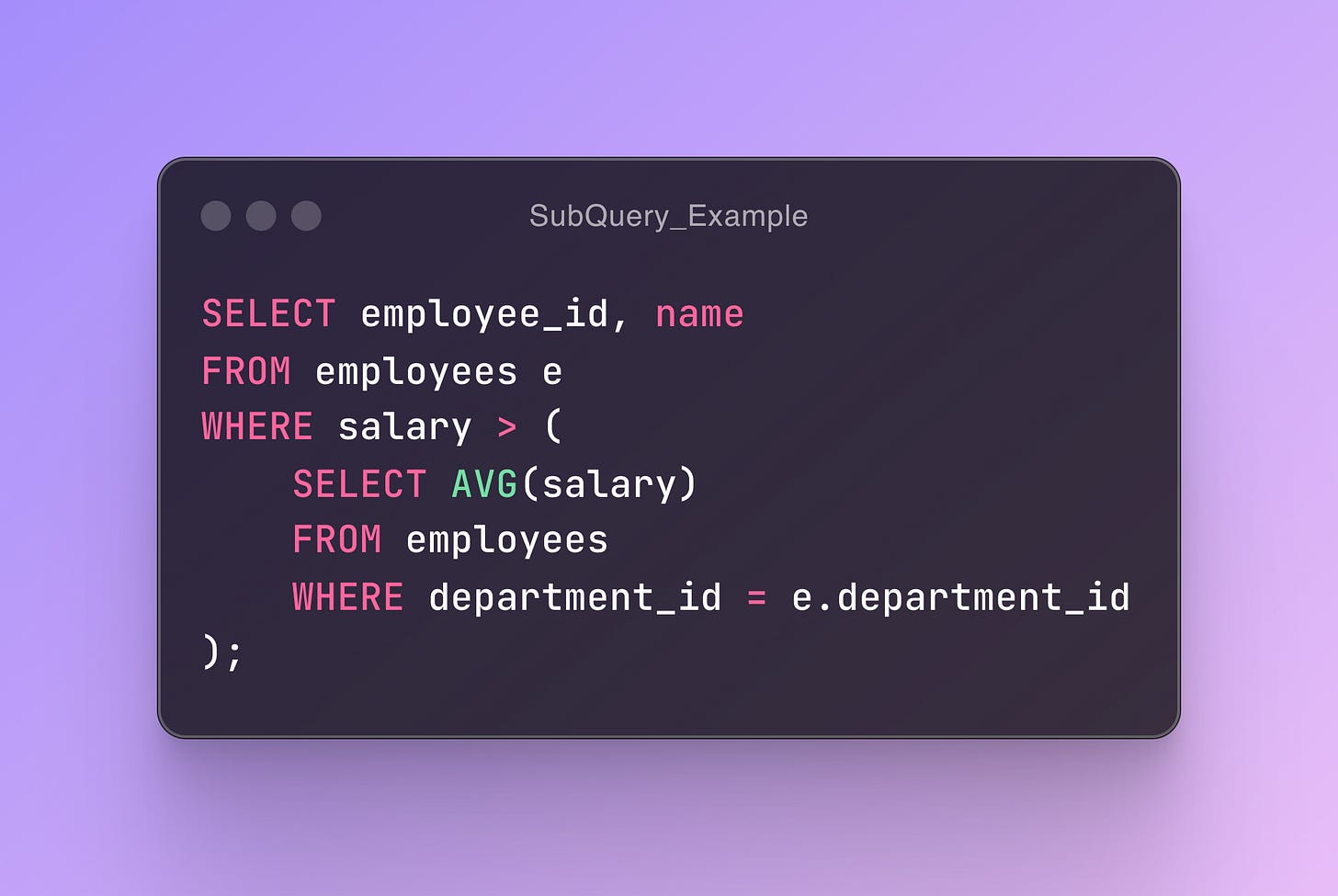
e.g. Consider the task of finding employees in a department with above-average salaries.
Using CTE:
Using Subquery:
Finally, to remember:
A CTE is executed only once per query. If you need to re-use the output of the CTE multiple times in the same query, then use CTE
A subquery can end up running multiple times as part of a larger query