SQL Collation: A Match Made in Query Heaven
Case Closed!
In SQL, collation refers to a set of rules that determines how strings of text are sorted and compared.
Collation is important when dealing with databases that store textual data in multiple languages or require specific case sensitivity or accent sensitivity.
Key Concepts of Collation:
Character Set:
This defines the set of characters that can be stored in a database (e.g., UTF-8, Latin1)
Sorting Rules:
Collation defines how characters are sorted (e.g., alphabetical order, case sensitivity, accent sensitivity)
Comparison Rules:
Collation determines how strings are compared for equality (e.g., whether
Ais equal toaor if accents likeéandeare treated as the same)
Types of Collation Sensitivities
Case Sensitivity:
Case-Sensitive (CS): Treats uppercase and lowercase letters as different (e.g.,
A≠a)Case-Insensitive (CI): Ignores case when comparing or sorting (e.g.,
A=a)
Accent Sensitivity:
Accent-Sensitive (AS): Distinguishes characters with accents (e.g.,
é≠e).Accent-Insensitive (AI): Ignores accents (e.g.,
é=e).
etc..
Syntax:
In SQL Server, collations are represented in names like:
SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
SQL_Latin1_General: The culture or or localeCP1: Code page (character set). which is a character encoding for Western European languagesCI: Case-insensitive.AS: Accent-sensitive.
So, SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS is a collation that:
Uses the general Western European culture.
Follows the Code Page 1252 encoding.
Is case-insensitive but accent-sensitive. This means it ignores case differences but considers accent differences when sorting or comparing text.
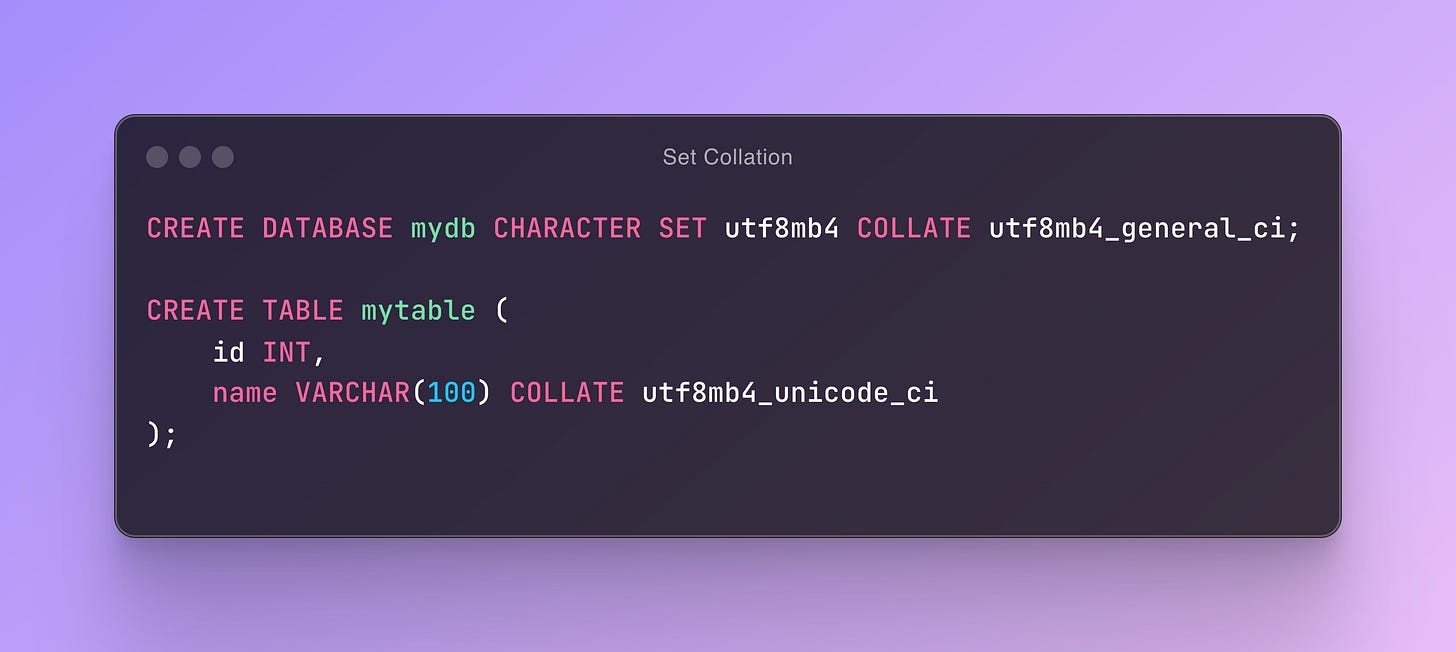
In MySQL, collations are typically used with character sets:
Character Set:
utf8mb4Collation:
utf8mb4_general_ci(general collation, case-insensitive).
Setting Collation for a Database/Table/Columns:
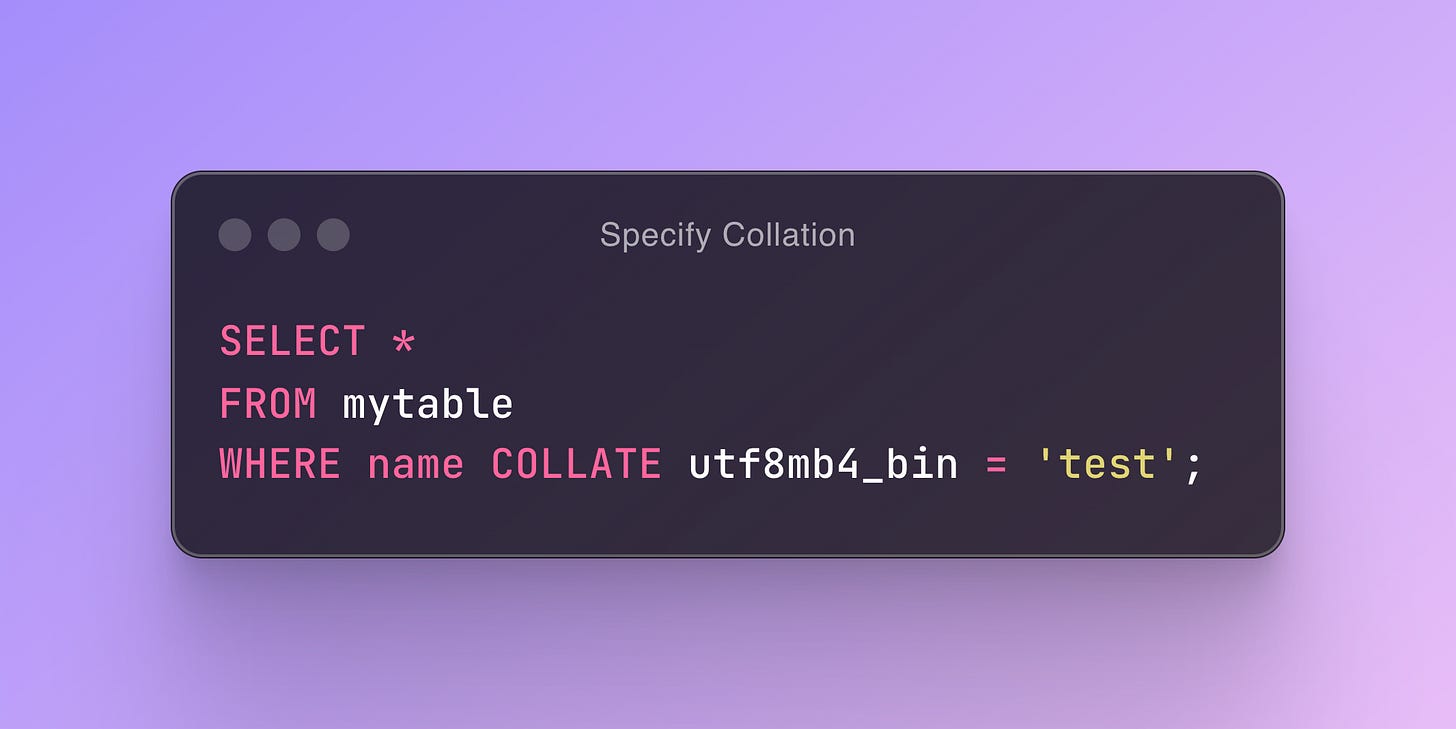
Specifying Collation in Queries:
Scenario Examples:
Case-Insensitive Comparison
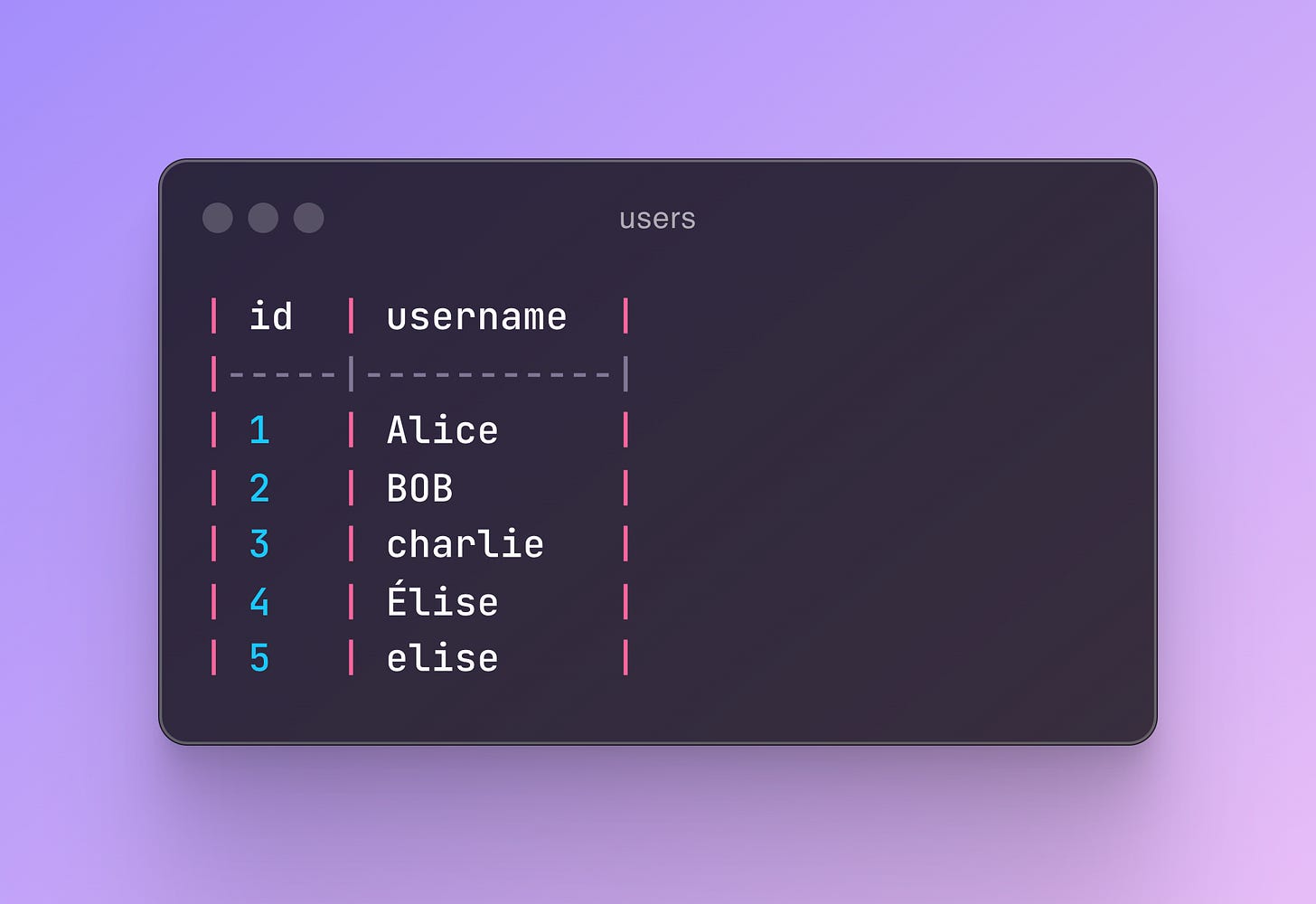
You have a table named users with the following data:
Now, you want to perform a case-insensitive search for the username bob.
Case-Sensitive Comparison
If you want the comparison to be case-sensitive, you can change the collation to a case-sensitive one: